
Products
Polystyrene sulfonic acid
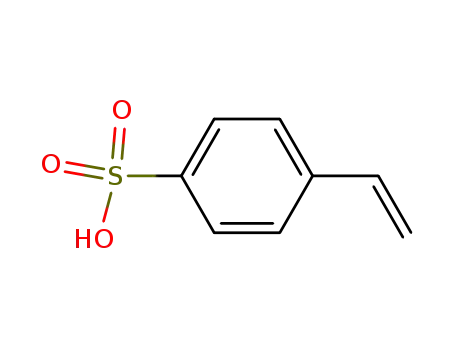
Synonyms:4-ethenylbenzenesulfonic acid;4-Styrenesulfonic acid;28210-41-5;98-70-4;4-vinylbenzenesulfonic acid;p-Vinylbenzenesulfonic acid;Benzenesulfonic acid, 4-ethenyl-;UNII-1D1822L42I;9080-79-9;1D1822L42I;styrene-4-sulphonic acid;MFCD00165973;Tolevamer [INN];UNII-ZSL2FB6GXN;SCHEMBL25711;CHEMBL1490300;DTXSID5045045;AKOS024462356;CS-0187639;FT-0660598;Q3395465
Chemical Property of Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid
● Appearance/Colour:Colorless to Yellow Liquid
● Melting Point:1°C
● Refractive Index:n20/D 1.3718
● Boiling Point:100°C
● Flash Point:°C
● PSA:62.75000
● Density:1.11 g/mL at 25 °C
● LogP:2.66760
● Storage Temp.:Sealed in dry,Room Temperature
● Solubility.:H2O: soluble
● Water Solubility.:Miscible with water, ethanol, methanol, lower alcohols and glycols.
● XLogP3:1.4
● Hydrogen Bond Donor Count:1
● Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count:3
● Rotatable Bond Count:2
● Exact Mass:184.01941529
● Heavy Atom Count:12
● Complexity:242
Useful
Chemical Classes:Plastics & Rubber -> Polymers
Canonical SMILES:C=CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)O
Recent NIPH Clinical Trials:Effects of calcium and sodium polystyrene sulfonate on mineral and bone metabolism in pre-dialysis patients with hyperkalemia
Uses:Polyelectrolyte. Electroconductive and antistatic resin for electrographic and electrophotographic substrates. Poly(p-styrenesulfonic acid) is a polymer used as a hole-?injecting electrode in polymer-?based light emitting devices.
Detailed Introduction
Polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSSA) is a highly sulfonated polystyrene polymer that contains sulfonic acid groups (-SO3H) attached to the polymer backbone. It is a water-soluble polymer with various applications in industries such as chemical synthesis, catalysis, and electronics. Here are some key details about polystyrene sulfonic acid:
Structure: Polystyrene sulfonic acid is typically synthesized by sulfonating polystyrene polymer with sulfuric acid or other sulfonating agents. This sulfonation results in the replacement of some hydrogen atoms with sulfonic acid groups (-SO3H) along the polymer backbone. The degree of sulfonation can be controlled to obtain polymers with different ion exchange capacities and solubility properties.
Water Solubility: Polystyrene sulfonic acid exhibits high water solubility due to the presence of sulfonic acid groups that enhance its polarity. This property makes it easy to handle and use in various applications, as it can be readily dissolved or dispersed in water-based systems.
Ion Exchange Properties: Polystyrene sulfonic acid is known for its strong acidic properties due to the sulfonic acid groups. It can act as an ion exchange resin, where the sulfonic acid groups can exchange with other cations or anions present in a solution. This property makes it useful in applications such as water treatment, ion separation, and purification processes.
Catalysis: The sulfonic acid groups in polystyrene sulfonic acid make it an effective catalyst in various chemical reactions. It can catalyze esterification, alkylation, and other acid-catalyzed reactions. The acidic nature of PSSA facilitates proton transfer reactions, leading to increased reaction rates and selectivity.
Electrolytes in Fuel Cells: Polystyrene sulfonic acid-based polymers have been investigated as proton-conducting electrolytes in fuel cells. Their high proton conductivity, water solubility, and stability at elevated temperatures make them potential candidates for use in fuel cell membranes.
Polymer Electrolyte Membranes: Polystyrene sulfonic acid can be utilized as a component in polymer electrolyte membranes for various electrochemical devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors. The sulfonic acid groups allow for ion transport within the membrane, enabling efficient charge transfer.
Surface Modification and Adhesion: Polystyrene sulfonic acid can be used to modify or functionalize surfaces of materials by providing sulfonic acid groups for chemical reactions or binding to target molecules. This property makes it useful in adhesive formulations, coatings, and surface modifications for biomedical and industrial applications.
Overall, polystyrene sulfonic acid is a versatile polymer with diverse applications due to its water solubility, ion exchange properties, catalytic activity, and potential use in electrochemical devices. Ongoing research continues to explore its properties, potential applications, and the development of new derivatives and formulations.
Application
Polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSSA) finds applications in various industries due to its unique properties. Here are some specific applications of PSSA:
Water Treatment: PSSA is used as an ion exchange resin in water treatment processes. It can remove unwanted ions, such as heavy metals, from water through ion exchange reactions.
Catalysis: PSSA is an effective catalyst in a range of chemical reactions, including esterification, alkylation, and condensation reactions. It can be used in organic synthesis and the production of specialty chemicals.
Electrochemistry: PSSA can be used as an electrolyte in electrochemical devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors. Its high proton conductivity enables efficient charge transfer in these devices.
Fuel Cells: PSSA-based membranes can be used as proton-conducting electrolytes in fuel cells. They facilitate the movement of protons while preventing the crossover of reactant gases, contributing to enhanced fuel cell performance and efficiency.
Adhesives and Surface Modification: PSSA can be utilized in adhesive formulations due to its ability to functionalize surfaces and promote adhesion. It can also be used for surface modification of materials to improve their properties, such as surface wettability and biocompatibility.
Biomedical Applications: PSSA has potential applications in biomedicine, including drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Its water solubility and ability to bind to biomolecules make it a versatile material for various biomedical applications.
Coatings and Paints: PSSA can be used in the formulation of coatings and paints to provide desired adhesion, rheological properties, and stability.
Textile Industry: PSSA can be employed in the textile industry for coloration and dye fixation. It can enhance the affinity of dyes to the textile fibers, resulting in improved colorfastness.
Analytical Chemistry: PSSA can be used as a stationary phase in chromatographic separations and as a modifier in chemical sensors for the detection of ions or molecules.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications for polystyrene sulfonic acid. The versatility of PSSA makes it a valuable material in various industries, offering solutions for a range of challenges and facilitating advancements in numerous fields.




![Phenol,2-[4,6-bis(2,4-diMethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]-5-Methoxy](https://cdn.globalso.com/pengnuochemical/Phenol2-46-bis24-diMethylphenyl-135-triazin-2-yl-5-Methoxy-1820-28-6.png)



