Products
Phenylurea
Synonyms:amino-N-phenylamide;N-phenylurea;urea, N-phenyl-;urea, phenyl-
Chemical Property of PHENYLUREA
● Appearance/Colour:off-white powder
● Melting Point:145-147 °C(lit.)
● Refractive Index:1.5769 (estimate)
● Boiling Point:238 °C
● PKA:13.37±0.50(Predicted)
● Flash Point:238°C
● PSA:55.12000
● Density:1,302 g/cm3
● LogP:1.95050
● Storage Temp.:Store below +30°C.
● Solubility.:H2O: 10 mg/mL, clear
● Water Solubility.:Soluble in water.
● XLogP3:0.8
● Hydrogen Bond Donor Count:2
● Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count:1
● Rotatable Bond Count:1
● Exact Mass:136.063662883
● Heavy Atom Count:10
● Complexity:119
● Transport DOT Label:Poison
Purity/Quality
99% *data from raw suppliers
Phenylurea >98.0%(HPLC)(N) *data from reagent suppliers
Safty Information
● Pictogram(s):
● Hazard Codes:Xn
● Statements:22
● Safety Statements:22-36/37-24/25
Useful
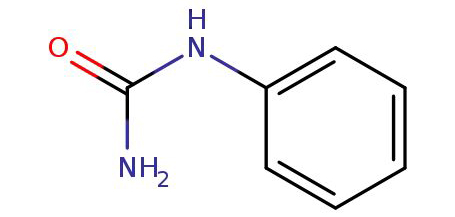
● Canonical SMILES: C1=CC=C(C=C1)NC(=O)N
● Uses: Phenylureas are commonly used soil-applied herbicides for control of grass and small-seeded broadleaf weeds. Phenyl urea is used in organic synthesis. It acts as an efficient ligand for palladium-catalyzed Heck and Suzuki reactions of aryl bromides and iodides.
Phenylurea, also known as N-phenylurea, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C7H8N2O. It is an organic compound belonging to the class of urea derivatives. Phenylurea is derived from urea by substituting one of the hydrogen atoms with a phenyl group (-C6H5).Phenylurea is primarily used as an additive in agricultural and horticultural applications. It is commonly used as a plant growth regulator, which helps in enhancing the growth and yield of various crops. Phenylurea can promote cell division, improve water and nutrient absorption, and regulate a plant's response to stressors. It is particularly effective in stimulating fruit set and ripening in crops like grapes and tomatoes.In addition to its agricultural use, phenylurea is also employed in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It can serve as a starting material or reagent in various chemical reactions.As with any chemical compound, it is essential to handle phenylurea with caution and follow appropriate safety measures.