
Products
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
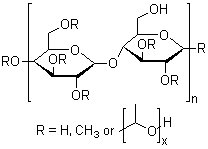
Synonyms:Metolose SH;DP 1208;Noigel 0215H;Methocel 20-333;Methocel 311;Viscontran MHPC 50;59029-31-1;HPMC;37341-76-7;Methocel 227;Methocel E;Benecel MP 943;Methocel 40-202;Methocel J;Goniosol;62683-26-5;Hypromellose;Methocel 856N;MC 400;Metolose;Accel R 100;Marpolose 60MP5;(HYDROXYPROPYL)METHYL CELLULOSE;Hydroxy?Propyl?Methyl?Cellulose;HYDROXYPROPYLMETHYL CELLULOSE(HPMC);HPMC-Industrial grade;Cellulose ether for PVC -Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose;2-HydroxyPropylMethylEther(Cellulos);Methyl Hydroxy Propyl Cellulose;hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose(HPMC);Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose;Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC);HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methyl cellulose);Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose;;HYDROXY PROPYL METHYL CELLULOSE??? (HPMC);Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose;Hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose;Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose(HPMC or MHPC);2-Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose;Marpolose MP 4000;Synchron-Oral;Methylhydroxypropylcellulosum;Hypromellosum [Latin];Methocel MK 4;Isopto Frin;Culminal 20000PFR;Methofas PM;8063-82-9;137397-89-8;Hipromelosa [Spanish];Cesca HPC 50;Marpolose EMP-H;Pharmacoat 645;Isopto Tears;HPMC(Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose);Hpmcd;Benecel MP 943W;71373-07-4;137397-91-2;171544-38-0;Estivin II;Methocel E, F, J, K;HPMC 20000PV;Methocel HG;Walocel MK 3.000PF;Methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose;Methocel F;DP 1209;Marpolose 90MP4000;Isopto alkaline;TC 5 (cellulose derivative);Hydroxypropylmethylcellulosum;Marpolose 65MP400;Walocel MW 60GA;Methocel 228;Courlose HPM;Pharmacoat 606;65607-39-8;TC 5E;Methocel E,F,K;Tearisol;Carbohydrate gum;HPM 100DS;Hipromelosa [INN-Spanish];125053-98-7;39363-71-8;Pharmacoat 603;Pharmacoat HPMC 615;Marpolose 90MP15000;Celacol HPM 5000;MOPTs;Celacol HPM 450;12673-53-9;Ultra Tears;137397-90-1;Methocel 240S;Marpolose 65MP4000;Cellulose,ethers,2-hydroxypropyl methyl ether;Benecel MP 363C;Isopto plain;Cellulose hydroxypropyl methyl ether;Methocel 20-231;Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose;Culminal MHPC;CELLULOSE, 2-HYDROXYPROPYL METHYL ETHER (R=CH3; (CH3)2CH);68073-10-9;Methocel 4FM-PRG;Cellulose, 2-hydroxypropyl methyl ether;Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 1828;Synchron;EM 1100 (cellulose derivative);TC 5R;11106-33-5;Tears Naturale;Methyl cellulose, propylene glycol ether;2-Hydroxypropyl cellulose methyl ether;Methocel K;Hypromellosum [INN-Latin];
Chemical Property of Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose
● Appearance/Colour:white to off-white powder
● Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
● Melting Point:1.39
● Boiling Point:1101.5°C at 760 mmHg
● Flash Point:619.9°C
● PSA:0.00000
● Density:1.39
● LogP:0.00000
● Storage Temp.:room temp
● Solubility.:H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear to very faintly turbid, faintly yellow
● Water Solubility.:SOLUBLE
Safty Information
● Pictogram(s):
● Hazard Codes:
● Safety Statements:24/25
Useful
Description:Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is a propylene glycol ether of methylcellulose in which both hydroxypropyl and methyl groups are bound to the anhydrous glucose ring of cellulose by ether linkages. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is synthesized from methyl cellulose by the action of alkali and propylene oxide. The resultant product is a water soluble ether derivative of cellulose containing both methoxy and hydroxypropyl groups. The degree of substitution is 1.08 to 1.83 with the hydroxypropyl groups as the minor constituent. White to off-white fibrous powder or granules. Soluble in water and some organic solvents. Insoluble in ethanol, the aqueous solution has surface activity, forms a thin film after drying, and undergoes a reversible transition from sol to gel in turn by heating and cooling.
Uses:Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose is a gum formed by the reaction of propylene oxide and methyl chloride with alkali cellulose. it will gel as the temperature is increased in heating and upon cooling will liquefy. the gel temperature ranges from 60°c to 90°c, forming semifirm to mushy gels. it is used in bakery goods, dressings, breaded foods, and salad dressing mix for syneresis control, texture, and to provide hot viscosity. usage level ranges from 0.05 to 1.0%.
Indications:Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose belongs to the group of medicines known as artificial tears. It is used to relieve dryness and irritation caused by reduced tear flow. It helps prevent damage to the eye in certain eye diseases. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose may also be used to moisten hard contact lenses and artificial eyes. In addition, it may be used in certain eye examinations.
Detailed Introduction
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) is a derivative of cellulose, which is a natural polymer found in the cell walls of plants. HPMC is produced through a chemical modification process that involves treating cellulose with propylene oxide and methyl chloride.
HPMC is a white, odorless powder that is soluble in water and forms a clear, viscous gel when dissolved. It has a wide range of applications across various industries due to its unique properties.
Here are some key features of HPMC:
Thickening Agent: HPMC is a highly effective thickener and viscosity modifier. It can significantly increase the viscosity of liquids, making it useful in a wide range of products that require a thick or gel-like consistency.
Film-forming properties: HPMC can form a thin, flexible film when applied to surfaces. This property is often utilized in coatings, paints, and other applications that require a protective or barrier layer.
Water Retention: HPMC has excellent water retention properties, allowing it to retain moisture in formulations. This makes it useful in applications such as cement-based materials, where it can improve workability and reduce shrinkage.
Emulsion Stabilizer: HPMC can stabilize emulsions, preventing the separation of oil and water phases. It is commonly used in cosmetics and personal care products to maintain the stability and consistency of creams, lotions, and other emulsions.
Controlled Release Properties: HPMC can control the release of active ingredients, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry. It can form a gel matrix that slows down the release of drugs, providing controlled and sustained release over time.
Non-Toxic and Environmentally Friendly: HPMC is considered safe for use in various applications. It is non-toxic, biodegradable, and does not pose a risk to human health or the environment.
Overall, HPMC is a versatile and widely used ingredient in industries such as pharmaceuticals, construction, food, personal care, paints, and agriculture. Its ability to modify viscosity, retain moisture, stabilize formulations, and control release makes it a valuable additive with diverse applications.
Application
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) is a hydrocolloid derived from cellulose, a natural polymer found in the cell walls of plants. HPMC is commonly used in a wide range of industries due to its unique properties.
Here are some common applications of HPMC:
Pharmaceutical Industry: HPMC is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as a pharmaceutical excipient. It is used in tablet formulations as a binder, filler, and disintegrant. HPMC can improve the dissolution and bioavailability of drugs while providing controlled release properties.
Construction Industry: HPMC is commonly used in the construction industry as a thickener, water retention agent, and binder. It is added to cement-based products such as tile adhesives, grouts, plaster, and mortar to improve workability, water retention, and adhesion.
Food Industry: HPMC is used as an additive in the food industry where it acts as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier. It is used in products such as salad dressings, sauces, bakery fillings, and ice creams to improve texture, viscosity, and stability.
Personal Care Products: HPMC is utilized in personal care products such as creams, lotions, and shampoos as a thickener and viscosity modifier. It provides a smooth and creamy consistency to these products and enhances their stability.
Paints and Coatings: HPMC is added to water-based paints and coatings to improve their thickness, prevent sagging, and enhance adhesion. It also acts as a stabilizer and can improve the flow and leveling properties of the paint.
Agricultural Industry: HPMC is used in agricultural applications as a thickener and film-forming agent in sprays and coatings. It improves the adherence of pesticides and fertilizers to plant surfaces, enhancing their effectiveness.
Textile Industry: HPMC is employed in textile printing and dyeing processes as a thickener for printing pastes. It helps to control the viscosity of the printing paste and improve the sharpness and color yield of the printed design.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. Its versatility, stability, and non-toxic nature make it a widely used ingredient in various industries.





![4-propyl-[1,3,2]dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide](https://cdn.globalso.com/pengnuochemical/4-propyl-132dioxathiolane-22-dioxide-165108-64-5.png)

