
Products
1,3-Dimethylurea,96-31-1
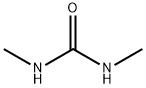
Dimethylurea Chemical Properties
| Melting point | 101-104 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point | 268-270 °C(lit.) |
| density | 1.142 |
| vapor pressure | 6 hPa (115 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4715 (estimate) |
| Fp | 157 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| pka | 14.57±0.46(Predicted) |
| form | Crystals |
| color | White |
| PH | 9.0-9.5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 765 g/L (21.5 ºC) |
| BRN | 1740672 |
| InChIKey | MGJKQDOBUOMPEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.783 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 96-31-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Urea, N,N'-dimethyl-(96-31-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3-Dimethylurea (96-31-1) |
Safety Information
| Risk Statements | 62-63-68 |
| Safety Statements | 22-24/25 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | YS9868000 |
| F | 10-21 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 400 °C |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29241900 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 96-31-1(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 4000 mg/kg |
Dimethylurea Usage And Synthesis
| Description | 1, 3-Dimethylurea is a urea derivative and used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is a colorless crystalline powder with little toxicity. It is also used for synthesis of caffeine, pharmachemicals, textile aids, herbicides and other. In the textile processing industry 1,3-dimethylurea is used as intermediate for the production of formaldehyde-free easy-care finishing agents for textiles. In the Swiss Product Register there are 38 products containing 1,3-dimethylurea, among them 17 products intended for consumer use. Product types are e.g. paints and cleaning agents. The content of 1,3-dimethylurea in consumer products is up to 10 % (Swiss Product Register, 2003). Use in cosmetics has been proposed, but there is no information available as to its actual use in such applications. |
| Chemical Properties | white crystals |
| Uses | N,N′-Dimethylurea can be used:
|
| Definition | ChEBI: A member of the class of ureas that is urea substituted by methyl groups at positions 1 and 3. |
| General Description | Colorless crystals. |
| Air & Water Reactions | Water soluble. |
| Reactivity Profile | 1,3-Dimethylurea is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). |
| Health Hazard | ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition 1,3-Dimethylurea emits toxic fumes. |
| Fire Hazard | Flash point data for 1,3-Dimethylurea are not available; 1,3-Dimethylurea is probably combustible. |
| Safety Profile | Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx |
| Purification Methods | Crystallise the urea from acetone/diethyl ether by cooling in an ice bath. Also crystallise it from EtOH and dry it at 50o/5mm for 24hours [Bloemendahl & Somsen J Am Chem Soc 107 3426 1985]. [Beilstein 4 IV 207.] |
Write your message here and send it to us









